Do Shower Filters Really Soften Water? (The Honest Answer)
Share
If you’ve ever browsed the shower-filter section online and seen phrases like “magnetic soft-water spheres,” “15-stage mineral re-energising”, or “ionised flow” — you’re not alone. The world of shower filters is full of marketing buzzwords that sound premium and holistic. But the key question is: do they actually soften water?
At Flowy, we believe you deserve clear answers — not mystery claims. Let’s dive in.
What is “soft water”?
“Soft water” is a technical term meaning water with low levels of the minerals calcium and magnesium — the ones that lead to scale build-up, soap not lathering properly, and that “sticky” feeling on skin or hair.
In most households, true water softening is done with a whole-house water softener (ion exchange system) that swaps calcium/magnesium for sodium or potassium. It’s a substantial piece of plumbing equipment.
So when you see a small shower filter claiming “soft water”, that’s the first sign to look closer at what’s really happening.
What a shower filter can do (and does well)
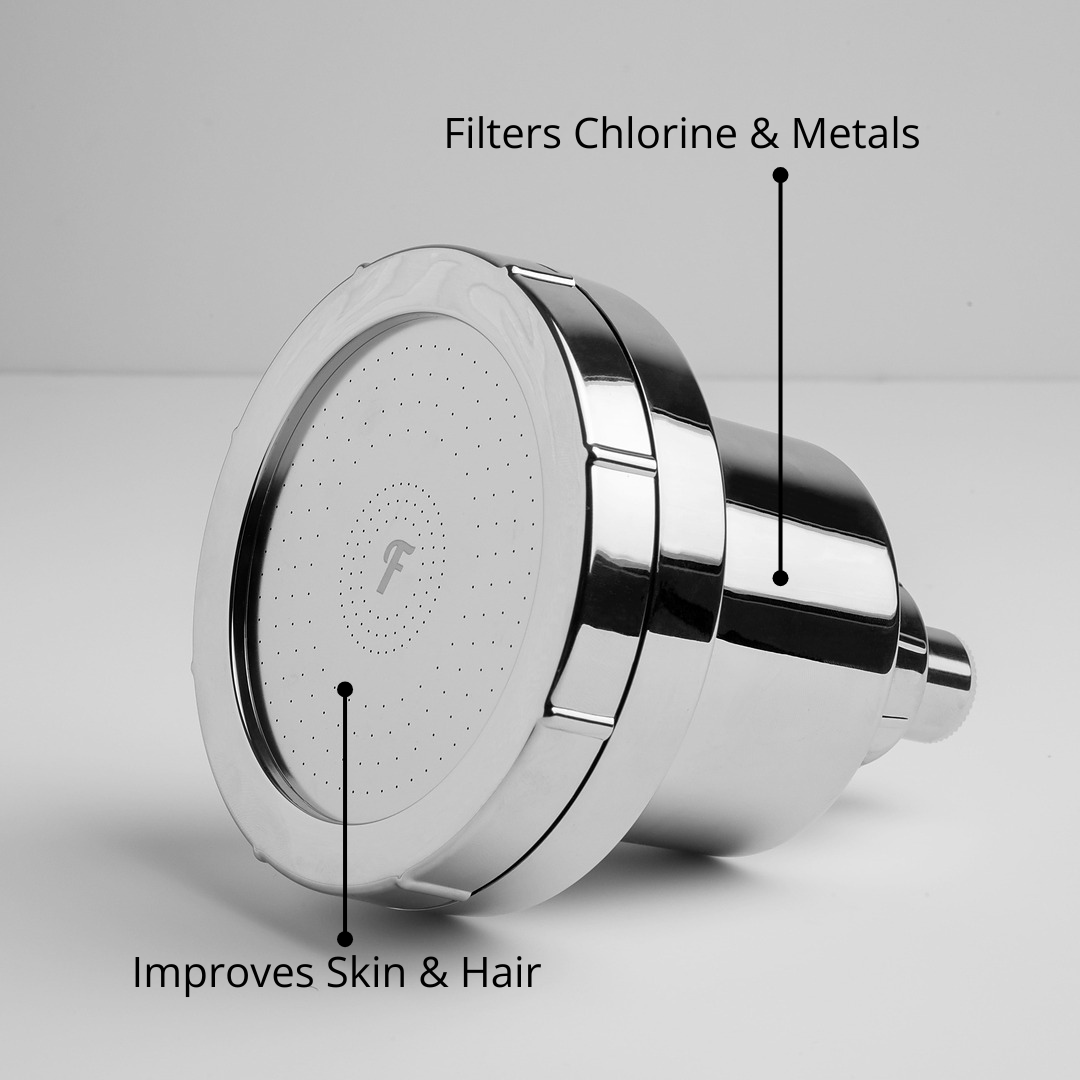
A good shower filter can make a real, visible difference to your showering experience — especially for skin and hair — even if it doesn’t technically remove the hardness minerals. Here’s how:
-
It can reduce chlorine, chloramines, heavy metals (lead, mercury, nickel) and other irritants using media like KDF-55, calcium sulphite, and catalytic carbon.
-
It can reduce sediment, rust, dirt, organic compounds and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
-
Less irritation means your skin and hair feel softer, even if the “hardness minerals” are still there.
For example: Australian retailers say their shower filters “reduce chlorine, heavy metals and impurities … resulting in healthier skin, softer hair and an overall better shower experience”.
Do shower filters soften water?
Short answer: Not in the technical sense of “softening” (i.e., removing calcium/magnesium minerals).
Multiple sources confirm this:
-
A deep dive article says: “Do Shower Filters Soften Water? No, shower filters can reduce the effect of hardness in water reducing the concentrations of calcium and magnesium.”
-
One Australian site explains that a whole-house water softener is required to remove hard-water minerals and prevent scale; whereas shower filters target contaminants.
That means when a shower filter claims “soft water” you need to check: are they removing hardness minerals? Or are they just improving feel by removing irritants?
Why the difference matters (and how we do it)
Here’s why this matters:
-
Transparency: If you think your filter is doing a whole-house softening job but it isn’t, you might feel mis-led.
-
Expectations: If you expect no scale or soap problems, you might be disappointed if the hardness minerals remain.
-
Credibility: Brands that over-promise can erode trust. At Flowy, we commit to what our filter realistically does for Australian water.
At Flowy, our approach is:
-
We remove the big irritants (chlorine, heavy metals, sediment) with proven media (KDF-55, calcium sulphite, catalytic carbon).
-
We deliver water that feels softer (because fewer irritants) rather than claiming we remove all hardness minerals.
-
We arm your customers with clear knowledge: “This filter improves how your water behaves and feels; for full hardness removal you need a different system”.
When you do need a full softener
If your home is facing:
-
major scale build-up on appliances and fixtures (kettles, taps, showers)
-
persistent soap/ shampoo lather issues across all outlets
-
large-scale plumbing damage from hardness minerals
… then a whole-house water softening system is likely the correct solution. A shower filter alone may improve feel but won’t swap out the hardness minerals themselves.
What you should look for in a quality shower filter
To get the best benefit (even if it’s not technically “softening”), check for:
-
Clear media listed (e.g., “KDF-55 + calcium sulphite + activated/catalytic carbon”)
-
Evidence of what the filter removes (chlorine, heavy metals, sediment)
-
Realistic claims (skin/hair benefit, feel improvement) rather than vague “ions” or “magnetic softening” language
-
Australian-friendly specs and installation ease
-
Clear cartridge replacement guidance
Understanding Hard Water and Its Mineral Content
Hard water is defined by its high mineral content, primarily due to elevated levels of calcium and magnesium ions. These essential minerals dissolve into water as it passes through mineral-rich rocks such as limestone and dolomite, contributing to the water’s hardness. The total hardness of water is often expressed as the sum of calcium and magnesium concentrations, measured in milligrams per litre (mg/L) or parts per million (ppm).
Types of Hardness: Temporary and Permanent
Water hardness can be categorized into two types: temporary hardness and permanent hardness. Temporary hardness is caused by dissolved bicarbonate minerals (calcium bicarbonate and magnesium bicarbonate) and can be reduced by boiling the water, which precipitates calcium carbonate, an insoluble substance that forms mineral deposits or scale. Permanent hardness is caused by calcium and magnesium salts such as calcium sulfate and magnesium chloride, which do not precipitate upon boiling and require water softening methods to remove.
Sources of Hard Water and Regional Variations
The mineral content of drinking water varies widely depending on local water supplies and geology. Surface water, such as rivers and lakes, generally contains lower mineral content compared to groundwater, which percolates through rocks and accumulates calcium and magnesium salts. In Australia, water hardness levels vary significantly, with areas like Western Australia experiencing higher hardness levels compared to regions with predominantly soft water such as parts of Tasmania and Victoria. The Australian Drinking Water Guidelines regulate water quality but do not mandate specific hardness levels, as hardness is not generally considered a public health risk.
Health Impacts of Drinking Hard Water
Drinking hard water contributes essential minerals like calcium and magnesium to the diet, which are vital for cardiovascular health, bone mineral density, and overall well-being. Several meta-analyses and studies published in international journals suggest an inverse relationship between drinking hard water and the risk of cardiovascular disease, potentially due to magnesium ions' protective effects on blood pressure regulation. However, excessive hardness levels may contribute to mineral deposits in the body, such as kidney stones, although evidence remains inconclusive.
Skin and Hair Health
Hard water can affect skin and hair by altering the natural oils that protect and hydrate the skin, often leading to dry skin and exacerbating conditions like atopic eczema. The presence of calcium and magnesium ions can cause soap scum formation, reducing the effectiveness of soaps and detergents and leaving the skin feeling dry or irritated. Using filtered water or shower filters can improve water quality, helping skin feel amazing and reducing dryness.
Water Softening and Shower Filters
Water softening is the process of reducing water hardness by removing calcium and magnesium ions, typically through ion-exchange systems that replace these divalent cations with sodium or potassium ions. Whole-house water softeners are effective in preventing calcium deposits and prolonging appliance life by reducing mineral scale buildup.
Shower filters, while not true water softeners, play an essential role in the filtration process by removing chlorine, heavy metals, and other contaminants from tap water. Many shower heads include filtration media such as KDF-55, calcium sulphite, and activated carbon, which help reduce irritants and improve the showering experience. Easy installation and environmentally friendly designs make these filters a popular choice for improving water quality and overall well-being.
Environmental and Practical Considerations
Using shower filters and water softeners can reduce mineral deposits and calcium deposits that clog plumbing and reduce water pressure. Some filters also remove fluoride and other harmful substances, contributing to cleaner, safer water. Regular cartridge replacement ensures optimal filtration performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the mineral content and hardness levels of your water supply is crucial for maintaining water quality, protecting plumbing systems, and supporting health. While drinking hard water provides essential minerals beneficial for preventive medicine and cardiovascular health, managing hardness through appropriate filtration and softening methods enhances skin health, reduces appliance damage, and ensures a better shower experience.
For those seeking to improve their water quality, investing in a quality shower filter or whole-house water softener offers an effective and environmentally friendly solution, aligning with Australian drinking water guidelines and promoting safe water use.
✅ Bottom line
Yes — a quality shower filter does make a difference. It can remove irritants and make your shower water feel softer, which improves skin and hair comfort.
No — it doesn’t act as a true water softener (in the sense of removing hardness minerals) unless explicitly designed for that purpose (and usually at whole-house level).
At Flowy, we believe in being clear about what our filter can do — and what it can’t. That way you make an informed decision and enjoy your shower every day.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does a shower filter make hard water soft?
Not technically. Shower filters remove chlorine, metals, and irritants that make water feel harsh, but true softening requires a whole-house ion exchange system.
What’s the best shower filter for hard water in Australia?
Look for one that uses KDF-55, Calcium Sulphite, and Catalytic Carbon — materials proven to reduce chlorine and heavy metals. Flowy’s Filter Plus blend is engineered specifically for Australian water conditions.
Can hard water cause dry skin or hair?
Yes. The minerals in hard water react with soap, forming residue that dries skin and dulls hair. Filtering out chlorine and impurities helps your natural oils rebalance, leaving skin softer and hair healthier.